See Dr. Sayed Monis at Neurosciences Centers Within 10 Days !
- 🧑⚕️ Orange Clinic: 714-562-8753 🧑⚕️ Brawley Clinic: 760-351-8669 🧑⚕️ El Centro Clinic: 760-592-4137 🧑⚕️ Imperial Clinic: 760-355-5248 🧑⚕️ Surgery Center: 760-355-6602
See Dr. Sayed Monis at Neurosciences Centers Within 10 Days !
Neuromodulation is a medical field that involves modulating the nerve activity through targeted delivery of electrical impulses or chemical agents to specific parts of the nervous system. It is often used as a therapeutic approach for managing chronic pain, neurological disorders, and other conditions that affect the nervous system.
The concept behind neuromodulation is that by manipulating nerve activity, either by stimulating or suppressing certain neural pathways, doctors can influence pain perception, motor function, and other bodily functions. Neuromodulation treatments can be minimally invasive, offering patients a non-surgical or less-invasive option to address chronic conditions. To learn more about neuromodulation for chronic pain relief, check out this page.
Diagnosis: To diagnose LBP, a healthcare professional will typically perform a physical exam, ask about medical history, and may order imaging tests such as X-rays or an MRI.
Mid Back Pain :Mid back pain refers to discomfort or pain located in the thoracic spine, the area between the bottom of the neck and the top of the lumbar spine.
Causes:
Herniated disc: A bulging or ruptured disc in the thoracic spine can press on nearby nerves, causing pain.
Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear of the cartilage in the thoracic spine can lead to inflammation and pain.
Spinal stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal in the thoracic region can compress the spinal cord and nerves, causing pain.
Fracture: A fracture in the thoracic vertebrae can cause severe pain.
Symptoms:
Diagnosis: Your doctor will likely perform a physical exam, ask about your medical history, and may order imaging tests such as an X-ray or MRI to determine the underlying cause of your pain.
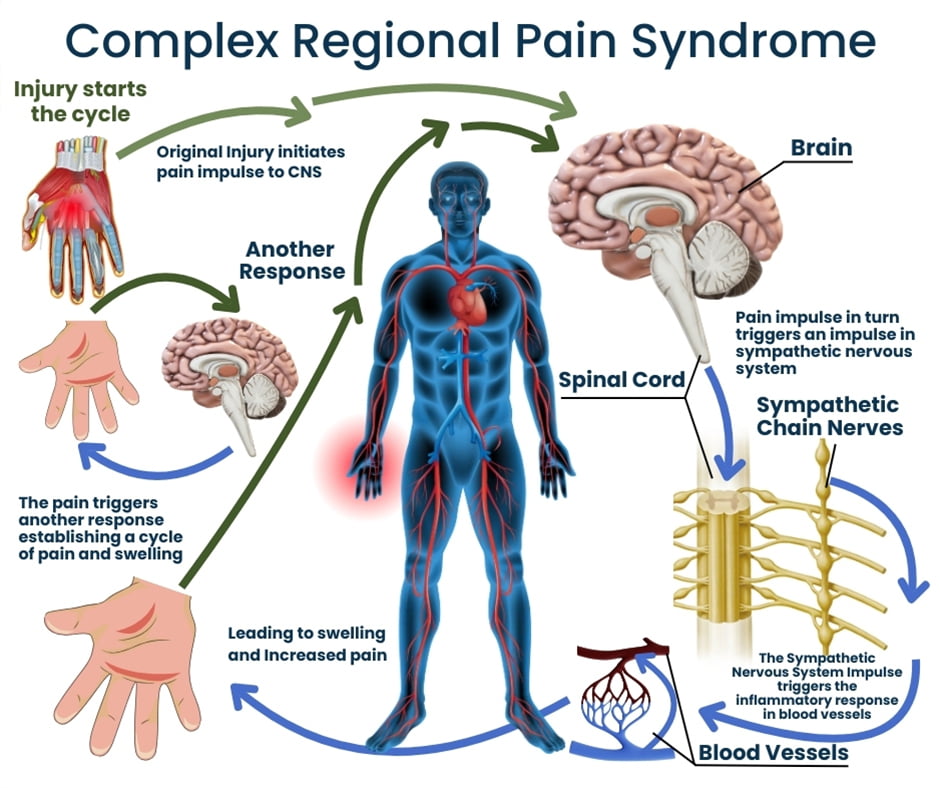
Chronic regional pain syndrome: is another term for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), a condition characterized by severe, persistent pain in a limb that is often triggered by an injury, even if seemingly minor, and results in pain disproportionate to the initial trauma, accompanied by changes in skin temperature, color, and swelling in the affected area; essentially, the body has an extreme reaction to the injury, causing ongoing pain and dysfunction in the limb.
Key points about CRPS:
other Neuralgia and Neurogenic disorders: Please consult for more details
Our approach at Neurosciences Centers commences with a detailed assessment of your medical history and pain profile. If deemed suitable for SCS, a trial period with a temporary electrode is initiated to gauge effectiveness.
State of the art facilities for chronic pain management and surgery. Neurosciences Centers is fully equipped to handle all your pain management needs.
A stroke, also known as a brain attack, occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to die.
The most common type, caused by a blood clot that blocks an artery in the brain
Occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, leading to bleeding in the brain.
Symptoms:
Symptoms can vary depending on the severity and location of the stroke, but may include:
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects movement. It is caused by the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in controlling muscle movement and coordination. As these neurons die, the brain’s ability to control smooth and coordinated movements is impaired, leading to a wide range of motor and non-motor symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors: The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is not entirely understood, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors appears to play a role. Some genetic mutations can increase the risk of Parkinson’s, though the majority of cases are sporadic. Exposure to certain toxins, age (usually diagnosed in people over 60), and family history are all factors that may increase one’s likelihood of developing the disease.
Common Symptoms:
A spinal cord injury (SCI) occurs when damage to the spinal cord disrupts the normal function of the nervous system, preventing the brain from sending signals to the body and vice versa. SCI can happen as a result of trauma, such as car accidents, falls, sports injuries, or violent events like gunshots, or it may develop from diseases like tumors, infections, or degenerative conditions affecting the spinal cord.
The severity of SCI depends on the location and extent of the injury. In general, injuries that occur higher up the spine tend to result in more significant impairment. A complete spinal cord injury results in a total loss of sensation and movement below the injury site, leading to paralysis. In contrast, an incomplete SCI allows some function or sensation to remain, though it may still cause significant motor and sensory deficits.
Common Symptoms:
Treatment Options:
Epilepsy is a chronic brain disorder that causes seizures, which are brief episodes of involuntary movement. Seizures occur when there’s an abnormal electrical discharge in the brain.
Headaches are a common neurological condition that can occur due to a number of possible reasons. A neurologist can help diagnose and treat headaches.
Types of headaches
A neurologist may perform a physical exam, review your medical history, and order tests such as:
Diabetic neuropathy is a complication of diabetes that damages the nerves, primarily in the feet, hands, legs, and arms.
Causes:
Symptoms:
Types:
Diagnosis:
Physical exam, Blood tests to check blood sugar levels, Nerve conduction study (NCS), and Electromyography (EMG).
Treatment:
Brain tumors are cancerous growths that can affect the brain and surrounding tissues. They can be malignant (cancerous) or benign (noncancerous).
Metastatic brain tumors
Movement disorders are neurological conditions that affect movement control, speed, and smoothness. They can involve too much movement, too little movement, or abnormal postures.
Memory disorders are conditions that affect memory, thinking, and behavior. They can be caused by brain injury, disease, or other factors.
Other memory disorders
Trigeminal neuralgia, also known as tic douloureux, is a chronic pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, the main sensory nerve in the face.
Causes: The exact cause of trigeminal neuralgia is unknown, but it is believed to be related to a compression or irritation of the trigeminal nerve by a nearby blood vessel or other structure.
Symptoms: Trigeminal neuralgia typically causes sudden, severe, and excruciating pain on one side of the face. The pain is often described as: electric shock-like, stabbing, burning, and throbbing. The pain can be triggered by everyday activities such as brushing teeth, washing the face, or eating. It may also occur spontaneously.
Diagnosis: A doctor can diagnose trigeminal neuralgia based on a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as an MRI or CT scan.
Nerve blocks, Surgery, and Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS).
Prognosis: Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic condition, but it can be managed with treatment. Most people with trigeminal neuralgia experience periods of remission between pain episodes.