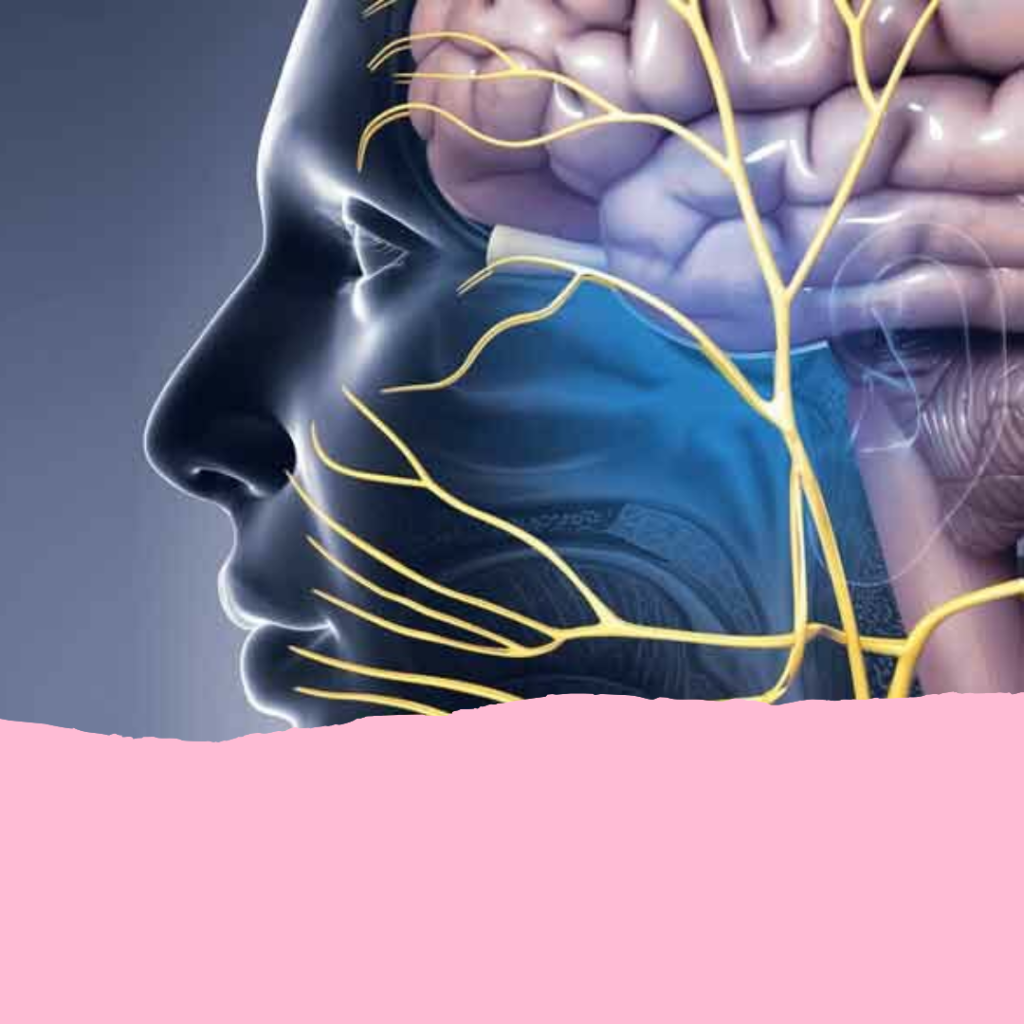
Trigeminal neuralgia, a debilitating neurological condition characterized by severe facial pain, can turn everyday activities into overwhelming challenges. Often described as one of the most excruciating pains known to medical science, it affects daily communication, eating, and even slight facial movements. Despite its intensity, there is hope and various treatment options available that can dramatically improve quality of life. This blog post aims to explore these treatments comprehensively, offering insight and encouragement to those seeking relief. We will delve into the latest advancements in medical science that promise even more effective solutions in the future, providing a beacon of hope for many.
Understanding Trigeminal Neuralgia
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Trigeminal neuralgia causes sudden bouts of sharp, stabbing pain that can strike the cheeks, jaw, teeth, gums, lips, or even the eyes and forehead. The pain is typically felt on one side of the face and can be triggered by mild stimulation. Accurately diagnosing trigeminal neuralgia involves a detailed medical history and physical examination, supported by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to rule out other causes and to detect any neurovascular compression.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of trigeminal neuralgia is usually a blood vessel pressing on the trigeminal nerve at the base of the brain. This pressure causes the nerve to malfunction and send pain signals. Factors that may increase the risk of developing trigeminal neuralgia include age (it is more common in people over 50), multiple sclerosis, and certain genetic predispositions.
Current Treatment Options
Trigeminal neuralgia, although challenging, can be managed effectively with the right treatment approach. The goal of treatment is not only to alleviate pain but also to improve the quality of life for sufferers. Options range from medications that can dampen or block the pain signals to surgical procedures that address the underlying cause of nerve irritation. This section will explore both well-established and newer methods, offering a comprehensive view of how those affected can find relief.
Medication Strategies
Medications are often the first line of defense against trigeminal neuralgia. Anticonvulsant drugs, such as carbamazepine and gabapentin, are commonly prescribed because they are effective at dampening nerve activity and reducing pain. For some patients, antispasmodic agents may also be recommended. These medications can help manage pain but might come with side effects that need careful management by healthcare providers.
Surgical Interventions
For cases where medication is ineffective or causes intolerable side effects, several surgical options are available. Microvascular decompression (MVD) is one of the most common surgical treatments. It involves moving or removing blood vessels that are compressing the trigeminal nerve. Other less invasive surgical options include Gamma Knife radiosurgery, which uses targeted radiation to damage the area of the trigeminal nerve that causes pain. These procedures have varying degrees of success and risks, which should be thoroughly discussed with a neurosurgeon.
Emerging Therapies and Research
The landscape of trigeminal neuralgia treatment is continually evolving, with promising research and innovative therapies on the horizon. This section will highlight the latest advancements in neurological research and the potential new treatments that are being developed, providing a glimpse into the future of managing this painful condition.
Advances in Neurological Research
Recent neurological research has focused on understanding the exact mechanisms behind trigeminal neuralgia, which has led to the identification of new potential targets for treatment. For instance, studies exploring the role of specific ion channels in the trigeminal nerve have opened up possibilities for new drug therapies that could more effectively block pain signals. Additionally, advancements in imaging technology have improved the accuracy of diagnosing the exact cause of nerve compression, allowing for more targeted surgical interventions.
Promising New Treatments on the Horizon
Alongside pharmaceutical advancements, there are several experimental treatments being tested that could revolutionize the management of trigeminal neuralgia. One such area is gene therapy, which aims to treat the pain at its molecular roots by altering the way pain signals are transmitted to the brain. Another exciting development is the use of high-focused ultrasound, a non-invasive technique that uses sound waves to target and destroy problematic areas of the nerve, providing pain relief without the need for incisions.
Managing Daily Life with Trigeminal Neuralgia
Living with trigeminal neuralgia requires adjustments to manage pain and maintain quality of life. This section will explore how lifestyle modifications and support systems can be vital tools in coping with the condition, allowing individuals to navigate their daily routines more comfortably.
Lifestyle Modifications
Managing trigeminal neuralgia effectively often involves making several lifestyle changes to reduce the frequency and severity of pain episodes. This can include identifying and avoiding triggers such as certain foods, drinks, or activities that provoke pain. Gentle facial exercises may be recommended to keep the muscles relaxed and prevent spasms. Additionally, stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can also play a crucial role in controlling pain, as stress can often exacerbate symptoms.
Coping Mechanisms and Support Systems
Developing strong coping strategies is crucial for dealing with the emotional and psychological impacts of trigeminal neuralgia. Support from family, friends, and support groups specifically for those with facial pain can provide emotional comfort and practical advice. Professional counseling may also be beneficial in helping patients develop resilience and coping strategies for living with chronic pain. Furthermore, connecting with online forums and communities can offer a sense of belonging and shared experience, which is invaluable.
Conclusion
Trigeminal neuralgia presents significant challenges, but the evolving landscape of treatment and management offers substantial hope. With the right combination of current treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and support systems, patients can lead fulfilling lives. Looking forward, the ongoing research and emerging therapies continue to brighten the outlook for those affected, promising even more effective solutions on the horizon.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the most promising areas of research in trigeminal neuralgia treatment?
Ans: Recent focuses include gene therapy, new pharmaceuticals targeting specific nerve pathways, and innovative surgical techniques like high-focused ultrasound.
Q: How can I participate in clinical trials for trigeminal neuralgia?
Ans: Contacting specialist neurological centers or hospitals and registering interest with organizations like the Facial Pain Association can help connect you to relevant clinical trials.
Q: Are there new treatments expected to be available soon?
Ans: While the timeline for new treatments can vary, ongoing clinical trials and research are continuously working towards new therapies, which could be available in the coming years.
Q: How do I find a support group for trigeminal neuralgia?
Ans: Many hospitals and online platforms offer resources to connect with support groups. Organizations dedicated to facial pain also provide directories of local and online support options.
Q: What lifestyle changes can specifically benefit someone with trigeminal neuralgia?
Ans: Avoiding known triggers, practicing stress reduction techniques, and implementing gentle facial exercises can significantly manage and reduce pain episodes.